Famous examples of the scientific method in ecology answer key – The scientific method is a cornerstone of ecological research, providing a systematic approach to understanding the complex interactions within ecosystems. Famous examples of its application have shaped our understanding of ecological processes and continue to inspire scientific inquiry.
This guide delves into the intricacies of the scientific method in ecology, showcasing groundbreaking studies that have advanced our knowledge and illuminated the intricate web of life.
Introduction to the Scientific Method in Ecology
The scientific method is a systematic approach to investigating and understanding the natural world. It is based on the idea that all phenomena are natural and can be explained through empirical evidence. In ecology, the scientific method is used to study the interactions between organisms and their environment.
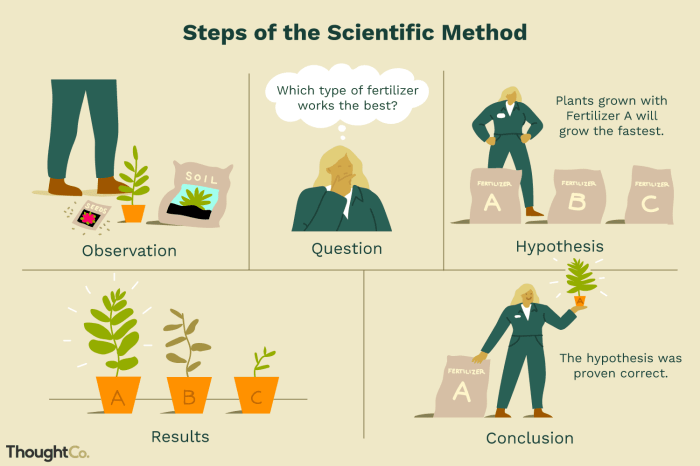
The key steps involved in the scientific method are:
- Observation: Making careful observations of the natural world.
- Question: Formulating a question based on the observations.
- Hypothesis: Developing a hypothesis, which is a tentative explanation for the question.
- Prediction: Making a prediction based on the hypothesis.
- Experiment: Conducting an experiment to test the prediction.
- Analysis: Analyzing the results of the experiment.
- Conclusion: Drawing a conclusion based on the analysis.
Observational Studies in Ecology: Famous Examples Of The Scientific Method In Ecology Answer Key

Observational studies are a type of research in which scientists make observations of organisms and their environment without manipulating or interfering with them. Observational studies can be used to generate hypotheses, which can then be tested through experiments.
Examples of observational studies in ecology include:
- Observing the distribution of a species in relation to environmental factors.
- Observing the interactions between different species in a community.
- Observing the effects of pollution on a particular ecosystem.
Experimental Studies in Ecology

Experimental studies are a type of research in which scientists manipulate or interfere with the environment to test a hypothesis. Experiments are used to determine cause-and-effect relationships between variables.
To design an experiment to test a hypothesis in ecology, you need to:
- Identify the independent variable (the variable that you are manipulating).
- Identify the dependent variable (the variable that you are measuring).
- Create a control group, which is a group that is not exposed to the independent variable.
- Replicate the experiment, which means repeating the experiment multiple times to ensure that the results are reliable.
Modeling in Ecology
Modeling is a powerful tool that can be used to simulate ecological systems and predict their behavior. Models can be used to explore different scenarios and to test hypotheses.
There are many different types of models used in ecology, including:
- Population models: These models simulate the growth and decline of populations.
- Community models: These models simulate the interactions between different species in a community.
- Ecosystem models: These models simulate the interactions between organisms and their environment.
Applications of the Scientific Method in Ecology
The scientific method has been used to solve a wide range of ecological problems, including:
- Understanding the causes of species extinctions.
- Developing strategies to protect endangered species.
- Managing natural resources.
- Predicting the effects of climate change.
Expert Answers
What are the key steps involved in the scientific method?
The scientific method typically involves observation, hypothesis formulation, experimentation, data analysis, and conclusion.
How do observational studies contribute to ecological research?
Observational studies allow scientists to gather data on ecological phenomena without directly manipulating the environment, providing insights into natural patterns and relationships.
Why are controls and replication essential in ecological experiments?
Controls and replication help to ensure the validity of experimental results by minimizing bias and accounting for natural variation.