A negative aspect of the protected membrane roof is a topic that warrants exploration, as it sheds light on the potential drawbacks and limitations associated with this roofing system. Understanding these negative aspects is crucial for informed decision-making and effective roof management.
Protected membrane roofs offer several advantages, including durability, energy efficiency, and aesthetics. However, like any roofing system, they are not without their challenges. This article delves into the negative aspects of protected membrane roofs, examining their structural integrity, condensation management, maintenance requirements, thermal performance, and environmental considerations.
Structural Integrity and Durability
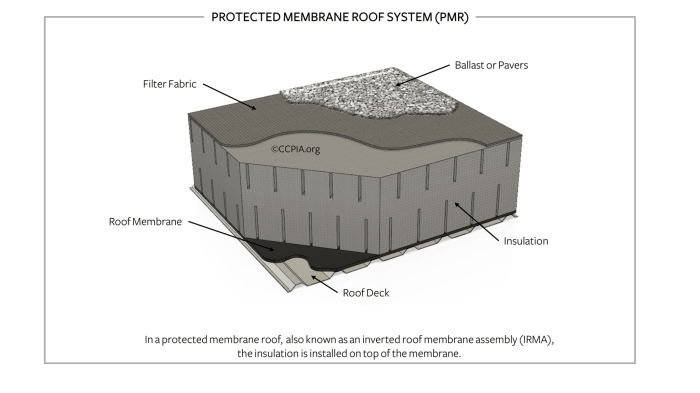
Protected membrane roofs are susceptible to punctures or tears, leading to leaks and reduced protection. Extreme weather conditions, such as high winds or hail, can also compromise the membrane’s integrity. Additionally, aging and UV exposure can degrade the membrane’s durability, making it more vulnerable to damage.
Punctures and Tears
- Sharp objects or debris can puncture or tear the membrane, creating leaks and compromising the roof’s integrity.
- Foot traffic and maintenance activities can also increase the risk of punctures or tears.
Extreme Weather Conditions, A negative aspect of the protected membrane roof is
- High winds can uplift the membrane, causing it to tear or detach from the roof structure.
- Hail can puncture or dent the membrane, leading to leaks and potential damage to the underlying roof components.
Aging and UV Exposure
- Over time, the membrane can deteriorate due to UV exposure and weathering, making it more susceptible to damage.
- Aging can also weaken the membrane’s seams and joints, increasing the risk of leaks.
Condensation and Moisture Management
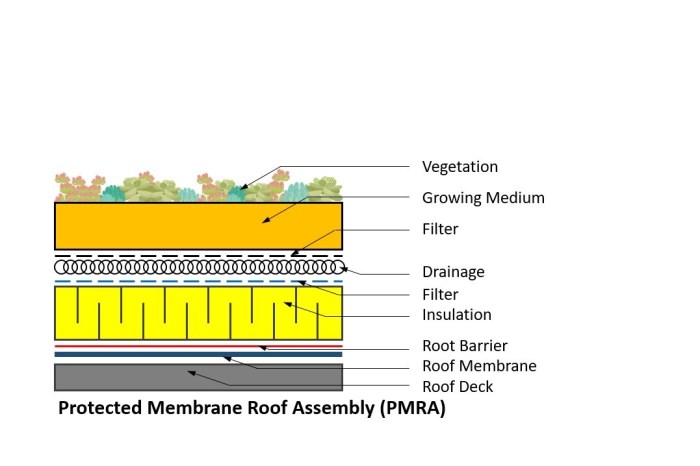
Condensation can form beneath the membrane, leading to moisture buildup and potential damage to the roof structure. Effective ventilation systems are crucial for mitigating condensation and maintaining a dry environment.
Condensation Formation
- Moisture from the interior of the building can condense on the underside of the membrane, especially during cold weather.
- Poor ventilation can trap moisture beneath the membrane, leading to mold growth and damage to the roof components.
Ventilation Systems
- Proper ventilation systems are essential for removing moisture and preventing condensation.
- Ventilation openings should be placed strategically to allow air to circulate beneath the membrane.
Best Practices
- Install a vapor barrier beneath the insulation to prevent moisture from reaching the membrane.
- Ensure adequate ventilation openings to allow air to circulate and remove moisture.
- Monitor the roof for signs of condensation and address any issues promptly.
Maintenance and Repair Costs
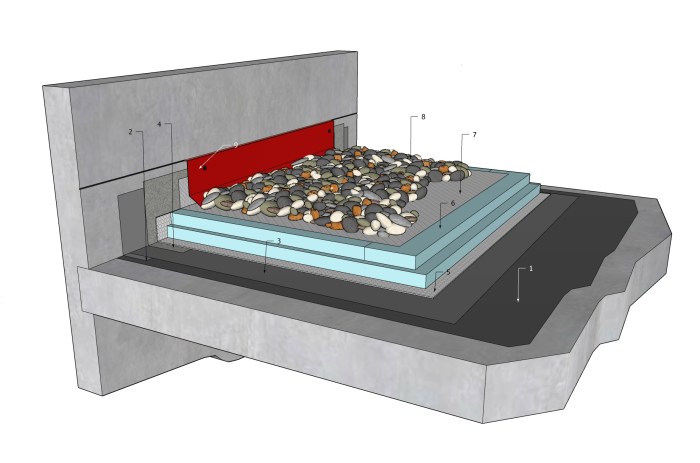
Protected membrane roofs require regular maintenance and repairs to ensure their longevity. The maintenance requirements and repair costs can vary depending on the type of membrane and the roof’s condition.
Maintenance Requirements
- Regular inspections are essential to identify potential problems and prevent major damage.
- Cleaning and debris removal can help prevent punctures and tears.
- Periodic recoating or patching may be necessary to maintain the membrane’s integrity.
Common Repair Issues
- Punctures or tears in the membrane require immediate repair to prevent leaks.
- Deteriorated seams or joints can lead to leaks and require repair or replacement.
- Ponding water on the roof can cause the membrane to stretch or tear, necessitating repairs.
Impact of Deterioration
- Membrane deterioration can increase the frequency of repairs and reduce the overall lifespan of the roof.
- Neglected repairs can lead to more extensive damage and costly replacements.
Essential FAQs: A Negative Aspect Of The Protected Membrane Roof Is
What are the common structural integrity issues associated with protected membrane roofs?
Protected membrane roofs may be susceptible to punctures or tears in the membrane, leading to leaks and reduced protection. Extreme weather conditions, such as high winds or hail, can also impact the membrane’s integrity.
How can condensation affect protected membrane roofs?
Condensation can form beneath the membrane, leading to moisture buildup and potential damage. Ventilation systems are essential for mitigating condensation and maintaining a dry environment.
Are protected membrane roofs expensive to maintain?
Compared to other roofing systems, protected membrane roofs may require more frequent maintenance. Common repair issues include punctures, tears, and membrane deterioration, which can increase maintenance costs.
