Foundations of Government Lesson Quiz 1-1 embarks on an intellectual journey, exploring the fundamental principles that underpin the structures of government. This quiz delves into the historical evolution, key concepts, and contemporary applications of government foundations, inviting learners to engage with the very essence of governance.
From ancient civilizations to modern nation-states, the foundations of government have shaped the course of human history. This quiz unravels the intricacies of popular sovereignty, limited government, and the separation of powers, providing a comprehensive understanding of the principles that govern our societies.
Introduction
The foundations of government establish the fundamental principles and structures upon which governments operate. They define the relationship between the governing body and the governed, ensuring the protection of individual rights and the effective functioning of society.
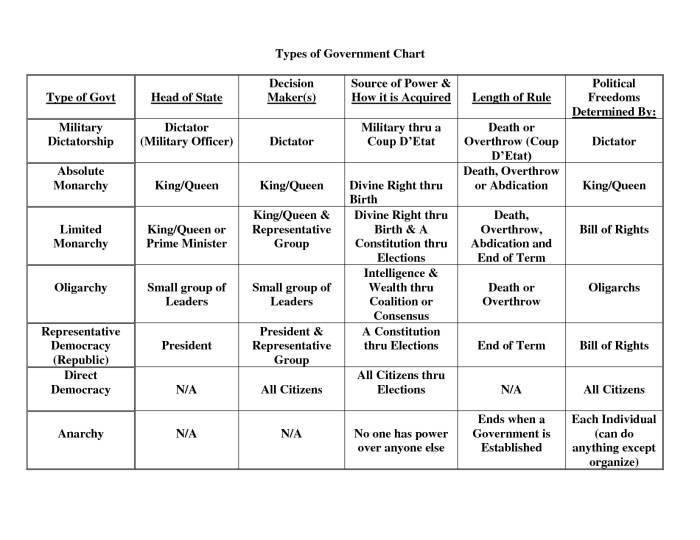
Different types of government foundations include monarchy, aristocracy, democracy, and oligarchy, each with its own unique characteristics and implications for citizen participation and accountability.
Key Principles, Foundations of government lesson quiz 1-1
Popular Sovereignty
Popular sovereignty is the concept that the authority of government derives from the consent of the governed. In a democracy, citizens hold the ultimate power to elect their leaders and hold them accountable.
Limited Government
Limited government refers to the idea that the power of the government is restricted by a constitution or other legal framework. This ensures that the government does not become tyrannical and that individual rights are protected.
Separation of Powers
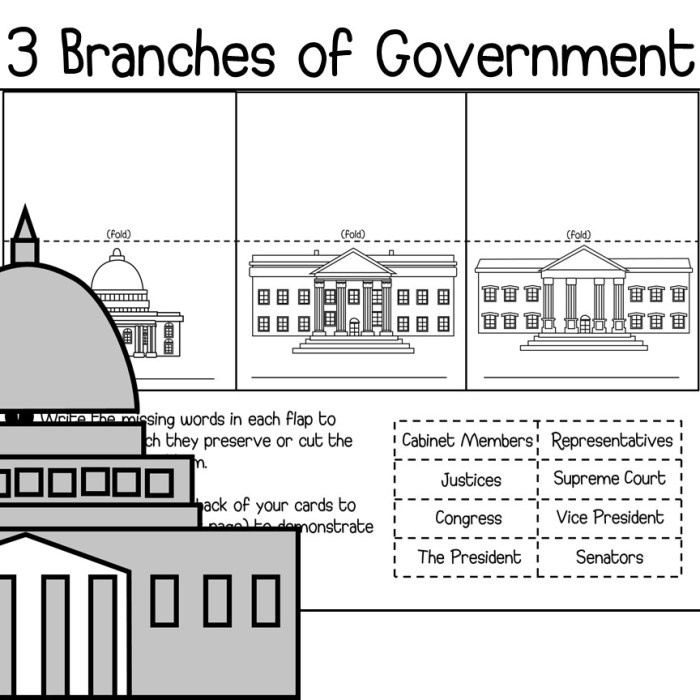
The separation of powers divides the powers of government among different branches, such as the executive, legislative, and judicial branches. This prevents any one branch from becoming too powerful and promotes checks and balances within the government.
Historical Context
Ancient Foundations
The foundations of government can be traced back to ancient civilizations, such as Greece and Rome. These societies developed systems of governance based on popular assemblies, elected officials, and written laws.
Enlightenment Influence
Enlightenment philosophers, such as John Locke and Montesquieu, greatly influenced the development of modern government principles. They emphasized the importance of individual rights, limited government, and the separation of powers.
Constitutional Government
Constitutional government is based on a written constitution that establishes the structure and powers of government. The first modern constitution was the United States Constitution, adopted in 1789.
Contemporary Applications
Digital Age Challenges
The digital age presents new challenges to government foundations, such as protecting privacy in the face of surveillance technologies and ensuring equal access to information and participation in the political process.
Social and Economic Well-being
Governments play a vital role in promoting social and economic well-being through policies such as education, healthcare, and social welfare programs.
Globalization
Globalization has increased interdependence among nations, leading to challenges for governments in regulating cross-border issues such as trade, environmental protection, and migration.
Q&A: Foundations Of Government Lesson Quiz 1-1
What is the significance of popular sovereignty?
Popular sovereignty is the principle that the government derives its power from the consent of the governed, ensuring that the authority of the state rests ultimately with the people.
How does limited government differ from authoritarian rule?
Limited government refers to a system where the powers of the state are restricted by a constitution or other legal framework, preventing the concentration of excessive authority in the hands of a single individual or entity.
What are the key elements of the separation of powers?
The separation of powers divides the functions of government into distinct branches, such as the executive, legislative, and judicial branches, to prevent any one branch from becoming too powerful.